Reference a KeyVault secret to an AppService setting on Azure

Table of Contents
Introduction #
The purpose of this post is to show how easy it is to reference a secret from a KeyVault on Azure, to an AppService environment variable, and how to deploy it all using Azure DevOps Pipelines and a Bicep template.
Using a KeyVault is the recommended way to store secrets on Azure, as it provides a secure, central store for the sensitive data needed by your applications (e.g. database passwords, certificates, etc.)
Infrastructure #
First, the infrastructure must be declared. The easiest and most readable way to do this, is with the new Azure Resource Manager DSL, Bicep.
The Bicep template below can be used to deploy three resources: An AppService plan, an AppService and a KeyVault.
The identity object on the Microsoft.Web/sites resource is important.
This is used to create a system assigned managed identity, that is being referenced when creating an access policy,
that allows the AppService to get secrets from the KeyVault.
Lastly, a secret named my-dirty-secret is being added to the KeyVault
(adding secrets to a KeyVault from a Bicep template is not a good idea if the Bicep template is stored
in e.g. a Git repository. The secret here is only for the purpose of showing how to reference it later on).
azure-resources.bicep
param location string = resourceGroup().location
var tenantId = 'INSERT_TENANT_UUID'
// List the name(s) of the app service(s) to deploy
var names = {
apps: [
'poc-service-dev'
]
}
var keyVaultSecrets = [
{ name: 'my-dirty-secret', value: 'Programming is like sex. One mistake and you have to support it for the rest of your life.' }
]
// Deploy the AppService Plan resource
resource appServicePlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2023-01-01' = {
name: 'app-vars-poc-plan'
location: location
sku: {
name: B1
capacity: 1
}
kind: 'linux'
properties: {
// must be set to true to get Linux host
reserved: true
}
}
// Deploy each app service to the AppService plan.
resource appServices 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2023-01-01' = [for appName in names.apps: {
name: '${appName}'
location: location
kind: 'app,linux'
identity: {
// Add system assigned managed identity to AppService.
// This must be added for the app service to be able to retrieve secrets from the KeyVault.
type: 'SystemAssigned'
}
properties: {
serverFarmId: appServicePlan.id
siteConfig: {
linuxFxVersion: 'JAVA|17-java17'
healthCheckPath: '/message'
numberOfWorkers: 1
vnetRouteAllEnabled: false
minTlsVersion: '1.2'
httpLoggingEnabled: false
ftpsState: 'Disabled'
}
httpsOnly: true
}
}]
// Setup KeyVault
resource keyVault 'Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults@2023-07-01' = {
name: 'kv-appvar-poc'
location: location
properties: {
sku: {
family: 'A'
name: 'standard'
}
tenantId: tenantId
enableSoftDelete: true
softDeleteRetentionInDays: 90
enabledForTemplateDeployment: true
}
}
// Add access policy for each app service, to allow getting secrets from KeyVault.
resource keyVaultAccessPolicies 'Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/accessPolicies@2023-07-01' = [for (appName, index) in names.apps: {
parent: keyVault
name: 'add'
properties: {
accessPolicies: [
{
tenantId: tenantId
objectId: appServices[index].identity.principalId
permissions: {
secrets: [
'get'
]
}
}
]
}
}]
// Insert secret to KeyVault.
resource secretsInKeyVault 'Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/secrets@2023-07-01' = [for secret in keyVaultSecrets: {
parent: keyVault
name: secret.name
properties: {
contentType: 'text/plain'
value: secret.value
}
}]
The bicep template above can be deployed from Azure DevOps with the following task declaration:
- task: AzureResourceManagerTemplateDeployment@3
displayName: Deploy infrastructure Bicep
inputs:
azureResourceManagerConnection: my-arm-service-connection
subscriptionId: $(subscription-id)
resourceGroupName: app-variables-poc
location: westeurope
csmFile: azure-resources.bicep
deploymentMode: Incremental
deploymentName: app-variables-poc-infra
Notice that the bicep file is referenced by the name azure-resources.bicep
After deployment, the resource group should contain three resources:
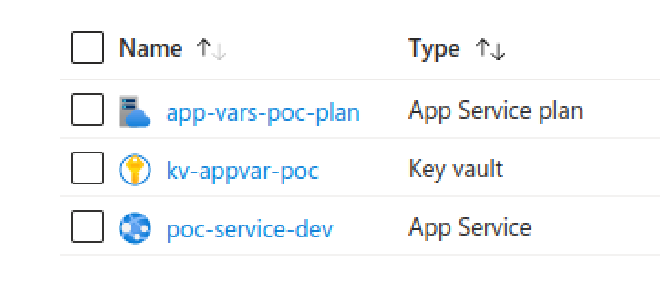
AppService deployment with secret reference #
Now imagine that our Azure DevOps pipeline has build the code for an application
and produced a pipeline artifact named app-service-artifact.zip
The application artifact can now be deployed to Azure with the task below. Notice how the AppSettings input
creates an application setting (environment variable) named MY_DIRTY_SECRET,
that is linked to the value of the secret that was just inserted into the KeyVault,
with the Bicep template from the
Infrastructure chapter.
# Download the produced artifact
- task: DownloadPipelineArtifact@2
inputs:
artifact: pipelineartifact
path: $(Pipeline.Workspace)/pipelineartifact
patterns: '**/*.zip'
# Deploy the AppService
- task: AzureRmWebAppDeployment@4
inputs:
appType: 'webApp'
azureSubscription: aau-its-rekv-dev-sc
packageForLinux: $(Pipeline.Workspace)/pipelineartifact/app-service-artifact.zip
ConnectionType: 'AzureRM'
WebAppName: poc-service-dev
AppSettings: -MY_DIRTY_SECRET @Microsoft.KeyVault(VaultName=kv-appvar-poc;SecretName=my-dirty-secret)
The application setting also shows up as a KeyVault reference in the Azure Portal:

Conclusion #
In this post, I’ve shown how to deploy an AppService and a KeyVault using Bicep templates, and how to reference a secret from a KeyVault when deploying an application artifact, using Azure DevOps.